Cost-Based Optimizer in Databricks
Spark SQL can use a Cost-Based Optimizer (CBO) to improve query plans. This is especially useful for queries with multiple joins. For this to work it is critical to collect table and column statistics and keep them up to date.
This functionality requires Databricks Runtime 3.3 or above.
Collect statistics
To get the full benefit of the CBO it is important to collect both column statistics and table statistics. Statistics can be collected using the Analyze Table command.
Tip
To maintain the statistics up-to-date, run
ANALYZE TABLE after writing to the table.Verify query plans
There are several ways to verify the query plan.
EXPLAIN command
Use the SQL Explain command to check if the plan uses statistics. If statistics are missing then the query plan might not be optimal. Below is the sample explain plan
== Optimized Logical Plan ==
Aggregate [s_store_sk], [s_store_sk, count(1) AS count(1)L], Statistics(sizeInBytes=20.0 B, rowCount=1, hints=none)
+- Project [s_store_sk], Statistics(sizeInBytes=18.5 MB, rowCount=1.62E+6, hints=none)
+- Join Inner, (d_date_sk = ss_sold_date_sk), Statistics(sizeInBytes=30.8 MB, rowCount=1.62E+6, hints=none)
:- Project [ss_sold_date_sk, s_store_sk], Statistics(sizeInBytes=39.1 GB, rowCount=2.63E+9, hints=none)
: +- Join Inner, (s_store_sk = ss_store_sk), Statistics(sizeInBytes=48.9 GB, rowCount=2.63E+9, hints=none)
: :- Project [ss_store_sk, ss_sold_date_sk], Statistics(sizeInBytes=39.1 GB, rowCount=2.63E+9, hints=none)
: : +- Filter (isnotnull(ss_store_sk) && isnotnull(ss_sold_date_sk)), Statistics(sizeInBytes=39.1 GB, rowCount=2.63E+9, hints=none)
: : +- Relation[ss_store_sk,ss_sold_date_sk] parquet, Statistics(sizeInBytes=134.6 GB, rowCount=2.88E+9, hints=none)
: +- Project [s_store_sk], Statistics(sizeInBytes=11.7 KB, rowCount=1.00E+3, hints=none)
: +- Filter isnotnull(s_store_sk), Statistics(sizeInBytes=11.7 KB, rowCount=1.00E+3, hints=none)
: +- Relation[s_store_sk] parquet, Statistics(sizeInBytes=88.0 KB, rowCount=1.00E+3, hints=none)
+- Project [d_date_sk], Statistics(sizeInBytes=12.0 B, rowCount=1, hints=none)
+- Filter ((((isnotnull(d_year) && isnotnull(d_date)) && (d_year = 2000)) && (d_date = 2000-12-31)) && isnotnull(d_date_sk)), Statistics(sizeInBytes=38.0 B, rowCount=1, hints=none)
+- Relation[d_date_sk,d_date,d_year] parquet, Statistics(sizeInBytes=1786.7 KB, rowCount=7.30E+4, hints=none)
Important
The
rowCount statistic is especially important for queries with multiple joins. If rowCount is missing, it means there is not enough information to calculate it (that is, some required columns do not have statistics).Spark SQL UI
Use the Spark SQL UI page to see the executed plan and accuracy of the statistics.

Missing estimate
A line such as
rows output: 2,451,005 est: N/A means that this operator produces approximately 2M rows and there were no statistics available.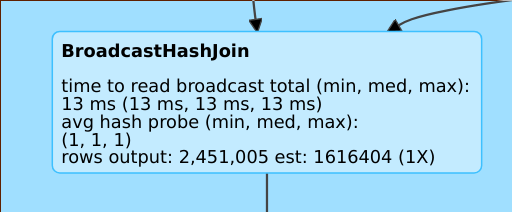
Good estimate
A line such as
rows output: 2,451,005 est: 1616404 (1X) means that this operator produces approx. 2M rows, while the estimate was approx. 1.6M and the estimation error factor was 1.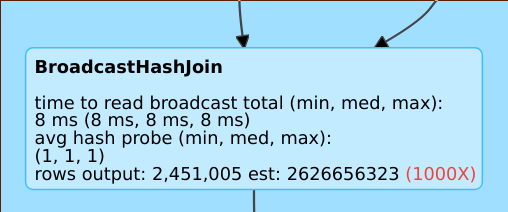
Bad estimate
A line such as
rows output: 2,451,005 est: 2626656323 means that this operator produces approximately 2M rows while the estimate was 2B rows, so the estimation error factor was 1000.Disable the Cost-Based Optimizer
The CBO is enabled by default. You disable the CBO by changing the
spark.sql.cbo.enabled flag.spark.conf.set("spark.sql.cbo.enabled", false)
Appreciate you sharing, great article.Much thanks again. Really Cool.
ReplyDeleteData Science Online Training